polarimeter equal but opposite|polarimetry explained : purchasing A pure (R)-enantiomer of a compound will rotate light in an equal but opposite direction as its (S)-enantiomer. If a mixture of compounds is racemic, meaning it contains an equal mixture of ( R . webTop 10 Best Burgers Near Toronto, Ontario. Sort:Recommended. Price. 1. Happy Burger. 4.6 (19 reviews) Hot Dogs. Burgers. $$ “Best burger I've had in a while and I love .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBPlaybonds.com é um site de jogos que oferece infinitas opções de diversão em um cassino 100% online, onde você pode reencontrar os clássicos jogos dos bingos, e curtir as .
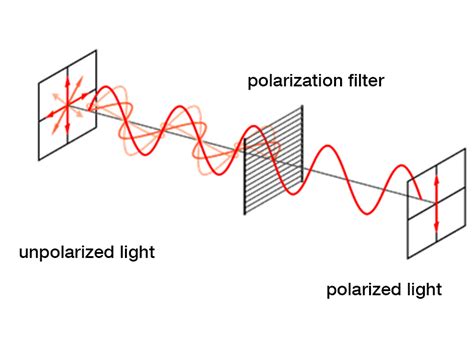
Each enantiomer of a stereoisomeric pair is optically active and has an equal but opposite-in-sign specific rotation. Specific rotations are useful in that they are experimentally determined constants that characterize and identify pure enantiomers.A polarimeter is an instrument which measures the angle of rotation by passing polarized light through an optically active (chiral) substance. To measure optical rotation, a Light Emitting Diode (LED) produces a beam of ordinary light.When plane-polarised light passes through some crystals, the velocity of left-polarized light is different from that of the right-polarized light, thus the crystals are said to have two refractive indices, i.e. double refracting. Construction: The polarimeter consists of a monochromatic source S which is placed at focal point of a convex lens L. Just after the convex lens there is a N.If the sample only rotates plane-polarized light half as much as expected, the optical purity is 50%. Because R and S enantiomers have equal but opposite optical activity, it naturally follows that a 50:50 racemic mixture of two .
A pure (R)-enantiomer of a compound will rotate light in an equal but opposite direction as its (S)-enantiomer. If a mixture of compounds is racemic, meaning it contains an equal mixture of ( R .Optical Activity. Optical activity is the ability of a chiral molecule to rotate the plane of plane-polairsed light, measured using a polarimeter. A simple polarimeter consists of a light source, .
POLARIMETRY and REFRACTOMETRY. Prof. Dr. Esra İbanoğlu. 1. Polarimeter. The technique used by polarimeter is called polarimetry, which is based on the rotation of polarized light (the . The rotation angles can be measured by using polarimeter (later in this section). For a pair of enantiomers with same concentration, under the same condition, they rotate the plane of polarization with the same angles but .
lifeproof s4 drop test
A polarimeter is an instrument used to determine the angle through which plane-polarized light has been rotated by a given sample. You will have the opportunity to use a polarimeter in the laboratory component of the course. . Because R .A pure (R)-enantiomer of a compound will rotate light in an equal but opposite direction as its (S)-enantiomer. If a mixture of compounds is racemic, meaning it contains an equal mixture of (R)- and (S)-enantiomers, then its optical rotation will be zero. Thus, polarimetry is a way to characterize and distinguish the identity between a pair of . The plane of polarization can be determined by an instrument called a polarimeter, . Because R and S enantiomers have equal but opposite optical activity, it naturally follows that a 50:50 racemic mixture of two enantiomers will have no observable optical activity. If we know the specific rotation for a chiral molecule, however, we can easily . Enantiomers have identical physical properties* , with one exception: enantiomers rotate plane-polarized light in equal and opposite directions, which is why they are sometimes called “optical isomers”. *(assuming an achiral environment) . (Prozac) is placed in a polarimeter. The observed rotation is 9.06° clockwise.
A polarimeter is an optical instrument with which one can accurately measure the angle by which the polarization of light is rotated e.g. when it passes through an optically active medium (containing chiral molecules). Operation Principle of Polarimeters. The basic operation principle of a polarimeter comprises the following:c. The numerical value of the optical rotation for enantiomers that are pure compounds is the same but opposite in sign (+or -). d. A polarimeter is not the only method to determine the specific rotation of a compound. 14. Which of the following statements is true concerning (-)-Mandelic Acid, which has a specific rotation − 15 8 ∘. Write .Optical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it travels through certain materials. Circular birefringence and circular dichroism are the manifestations of optical activity.Optical activity occurs only in chiral materials, those lacking .When rotation is quantified using a polarimeter it is known as an observed rotation, because rotation is affected by path length (l, the . Enantiomers will rotate the plane of polarisation in exactly equal amounts (same magnitude) but in opposite directions. Dextrorotary designated as d or (+), clockwise rotation (to the .
The plane of polarization can be determined by an instrument called a polarimeter, . Because R and S enantiomers have equal but opposite optical activity, it naturally follows that a 50:50 racemic mixture of two enantiomers will have no observable optical activity. If we know the specific rotation for a chiral molecule, however, we can easily .
The plane of polarization can be determined by an instrument called a polarimeter, . Because R and S enantiomers have equal but opposite optical activity, it naturally follows that a 50:50 racemic mixture of two enantiomers will have no observable optical activity. If we know the specific rotation for a chiral molecule, however, we can easily .
Equal but opposite!! Mixtures of Enantiomers These are high school mixture problems. If you know the specific rotation of the pure enantiomers and the composition of a mixture then the specific rotation of the mixture may be predicted. . The purpose of the study was to use the carbon targets and polarimeter detector system to measure the beam .They have equal but opposite optical rotations and recemize slowly at room temperature. The two structures are enatiomers of each other. They recemize too rapidly at room temperature for their optical rotations to be measured. . length of polarimeter = 1dm, wavelength = sodium D line, T = 25 o C. The specific rotation of camphor is .rotate the plane of plane-polarized light by equal amounts but in opposite directions Optical Activity. chiral compounds rotate the plane of plane-polarized light rotation measured in degrees clockwise (dextrorotatory or +) or counterclockwise (levorotatory or -) polarimeter - instrument for measuring optical activity Specific Rotation .They rotate plane-polarized light in equal but opposite directions. Isomer that rotates the plane to the left is (-) and called the levorotatory isomer. Other is dextrorotatory 2. They react at different rates with other chiral compound. . Polarimeter. instrument that is used to measure the optical rotation of your product. Optical Rotation.
What would be the [a] value of the opposite enantiomer? Answer. TBA. Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\) Apr 14, 2018, 10:50 AM. Problem SC7.2. A pure sample of the (+) enantiomer of compound B shows [a] = 32 o. What would be the observed a if a solution of the sample was made by dissolving 0.150 g in 1.0 mL of dichloromethane and was then placed in a 0 .
In this experiment you will learn how a polarimeter works and use one to measure the optical activity of limonene, sucrose, glucose, fructose and the hydrolysis of sucrose. . but in opposite directions. The amount and direction of rotation of polarized light . the (+) rotation from one enantiomer will exactly equal the (–) rotation from .When rotation is quantified using a polarimeter it is known as an observed rotation, because rotation is affected by path length (l, the . Enantiomers will rotate the plane of polarisation in exactly equal amounts (same magnitude) but in opposite directions. Dextrorotary designated as d or (+), clockwise rotation (to the .2) rotate the plane of plane-polarized light by equal amounts but in opposite directions. Optical Activity. chiral compounds rotate the plane of plane-polarized light rotation measured in degrees clockwise (dextrorotatory or +) or counterclockwise (levorotatory or -) polarimeter - instrument for measuring optical activity. Specific Rotation
A polarimeter is a scientific instrument used to measure the angle of rotation caused by passing polarized light through an optically active substance. The amount by which the light is rotated is known as the angle of rotation. . Each enantiomer of a stereoisomeric pair is optically active and has an equal but opposite-in-sign specific .
Diastereomers have different physical properties such as melting points, boiling points, densities, solubilities, refractive indices, dielectric constants and specific rotations. Enantiomers have similar physical properties except the opposite sign of specific rotation. Diastereomers other than geometrical isomers may or maynot be optically active.We know that enantiomers have identical physical properties and equal but opposite degrees of specific rotation. Diastereomers, in theory at least, have different physical properties – we stipulate ‘in theory’ because sometimes the physical properties of two or more diastereomers are so similar that it is very difficult to separate them.
Polarimeter The technique used by polarimeter is called polarimetry, which is based on the rotation of polarized light (the light after passing a polarizer) as it passes through a . enantiomers) will have no net rotation because the equal but opposite rotations cancel each other. The degree to which a substance rotates light may be used to .When rotation is quantified using a polarimeter it is known as an observed rotation, because rotation is affected by path length (l, the . Enantiomers will rotate the plane of polarisation in exactly equal amounts (same magnitude) but in opposite directions. Dextrorotary designated as d or (+), clockwise rotation (to the .If right-handed and left-handed species of a given molecule occurred with equal abundance, then there would be no net effect on the polarization of light passing through. . -handed or purely left-handed. However, these enantiomer compounds rotate light by exactly the same amount but in the opposite direction. The degree to which a substance .
When rotation is quantified using a polarimeter it is known as an observed rotation, because rotation is affected by path length (l, the . Enantiomers will rotate the plane of polarisation in exactly equal amounts (same magnitude) but in opposite directions. Dextrorotary designated as d or (+), clockwise rotation (to the .
Exercise 3.14. The specific rotation of (R)-limonene is +11.5 o in ethanol.What is the expected observed rotation of a sample of 6.00 g (S)-limonene dissolved in ethanol to a total volume of 80.0 mL in a 1.00 dm (10.0 cm) pathlength cuvette?Exercise 3.15. The specific rotation of (S)-carvone is +61 °, measured 'neat' (pure liquid sample, no solvent).The optical rotation of .
equal but opposite rotations. diastereomers in polarimeter. require experimental measurement. Racemic Mixture. 1:1 mixture of enantiomers. Resolution. The separation of a racemic mixture into its pure enantiomeric components. specific rotation [α] = observed rotation / .
polarimetry wiki
Resultado da 10 de ago. de 2022 · Primeiramente, o nome de Negrete é Matheus Nunes da Silva, humorista e influenciador. Com mais de dois milhões de seguidores .
polarimeter equal but opposite|polarimetry explained